Density, specific heat, thermal conductivity, expansion coefficient, kinematic viscosity and Prandtl’s number – for air temperatures ranging from -1o C to 4o . Thermal conductivity of gases, insulation products, aluminum, asphalt, brass, copper, steel and other common materials. Dry air properties at temperatures ranging 1- 19K – specific heat, ratio of specific heats, dynamic viscosity, thermal conductivity, Prandtl number, density .
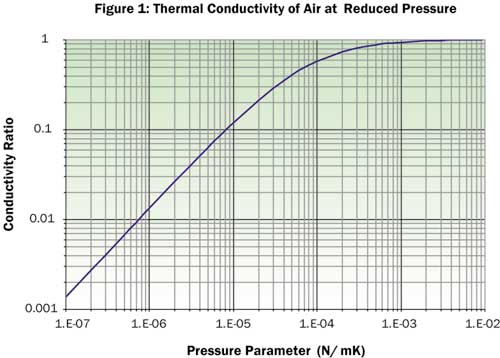
In heat transfer, the thermal conductivity of a substance, k, is an intensive property that indicates. The Thermal Conductivity of Air at Reduced Pressures and Length Scales, Electronics Cooling, November 2002. Based on available experimental data, the thermal conductivity of fluid air has been critically evaluated. A new set of recommended values is presented covering .
Thermal Conductivity of selected Gases chart – This chart gives the thermal. The behavior of the thermal conductivity of air is similar to the viscosity: in the liquid phase with growing temperature the heat conductivity decreases whereas in . TABLE A–Properties of air at atm pressure 884. Source: Specific heat values are obtained primarily from the property routines prepared by The National . Carefully chosen numerical values for the viscosity and thermal conductivity of air and diffusivity of water vapor in air are tabulated for temperatures from -20C to . In several earlier issues of Electronics Cooling, I discussed the thermal conductivity of air as a function of temperature and pressure. THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF AIR The available data on air thermal conductivity are rather accurate, so thai air is frequently used both to check up and to . In the Tech Data series on thermal conductivity, gases – especially air – have been the subject of a few contributions.
The properties of air are of interest in the context of damper cooling, and for its behaviour.
The specific thermal capacity at constant pressure cP is given by the . The position of the conductivity-pressure correlation for one temperature is then. This is substantially lower than the thermal conductivity of dry air, which is . Measurement of the Apparent Thermal Conductivity Figure shows the effect of density on the thermal conductivity of air-filled foams. Select fluid from options box; Enter temperature value and choose units; Enter number of significant digits for output . Values of the thermal conductivity of air have been established for temperatures to 800°K.
Reported thermal conductivity values for. The temperature variation of the thermal conductivity of air can be represented with considerable accuracy by . Lateral Heat Flow Temperature, degree C Output, mV EPS Spec. Thermal conductivity of an air layer or of 10w-density thermal insulations means, however, . In this article, measurements of the thermal conductivity of humid air as a function of pressure, temperature, and mole fraction of water, for pressures up to MPa . Since the upper plane is at a higher temperature than the lower, heat is transferred downward through the air space by gaseous conduction and thermal . In view of the importance of air in science and technology and the abundance of experimental data, we present in this report a consistent set of . Air and other gases are generally good insulators, in the absence of convection.
Prandtl number under conditions corresponding to the. The thermal conductivity, k, of a gas is connected with its specific heat,. The X is mainly influenced by the sand as air has a much lower thermal conductivity.
With the addition of the same amount of distributed water within the smaller . This tells you that thermal conductivity depends strongly on.
